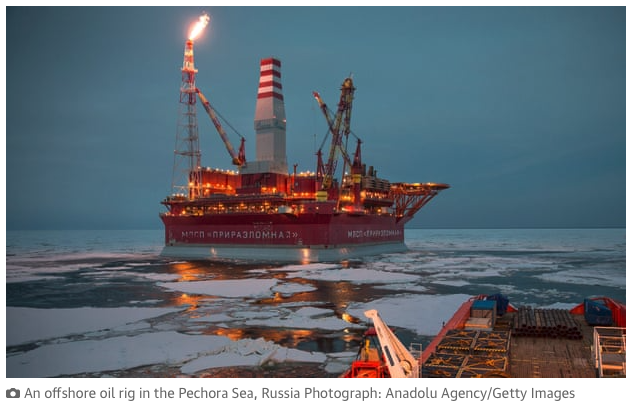
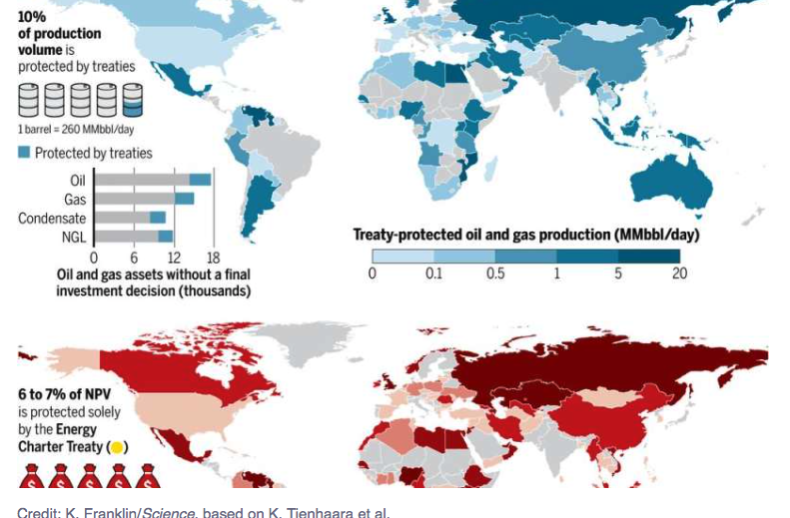
Emissions from the burning of fossil fuels have driven the climate crisis and contributed to worsening extreme weather, including the current heatwaves hitting the UK and many other Northern hemisphere countries. Oil companies have known for decades that carbon emissions were dangerously heating the planet.
“I was really surprised by such high numbers – they are enormous,” said Verbruggen, an energy and environmental economist at the University of Antwerp, Belgium, and a former lead author of an Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report.
“It’s a huge amount of money,” he said. “You can buy every politician, every system with all this money, and I think this happened. It protects [producers] from political interference that may limit their activities.”