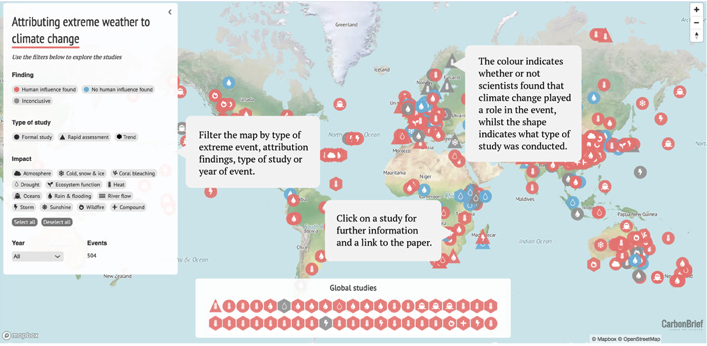
Known as “extreme event attribution”, the field has gained momentum, not only in the science world, but also in the media and public imagination. These studies have the power to link the seemingly abstract concept of climate change with personal and tangible experiences of the weather.
Scientists have published more than 400 peer-reviewed studies looking at weather extremes around the world, from wildfires in the US and heatwaves in India and Pakistan to typhoons in Asia and record-breaking rainfall in the UK. The result is mounting evidence that human activity is raising the risk of some types of extreme weather, especially those linked to heat.