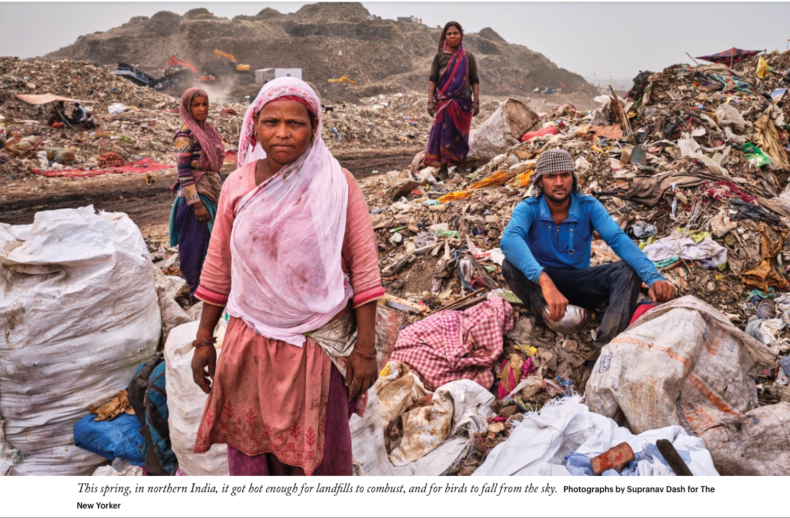
The Bhalswa landfill, on the outskirts of Delhi, is an apocalyptic place. A gray mountain of dense, decaying trash rises seventeen stories, stretching over some fifty acres. Broken glass and plastic containers stand in for grass and stones, and plastic bags dangle from spindly trees that grow in the filth. Fifteen miles from the seat of the Indian government, cows rummage for fruit peels and pigs wallow in stagnant water. Thousands of people who live in slums near the mountain’s base work as waste pickers, collecting, sorting, and selling the garbage created by around half of Delhi’s residents.
This March was the hottest on record in India. The same was true for April. On the afternoon of April 26th, Bhalswa caught fire. Dark, toxic fumes spewed into the air, and people living nearby struggled to breathe. By the time firefighters arrived, flames had engulfed much of the landfill. In the past, similar fires had been extinguished within hours or days, but Bhalswa burned for weeks. “The weather poses a big challenge for us,” Atul Garg, the chief of the Delhi Fire Service, said, nine days after the fire began. “Firefighters find it difficult to wear masks and protective gear because of the heat.” A nearby school, blanketed by hazardous smoke, was forced to close. In the end, it took two weeks to extinguish the blaze. The charred bodies of cows and dogs were found in the debris.